Solutions networkx#
Exercise 1#

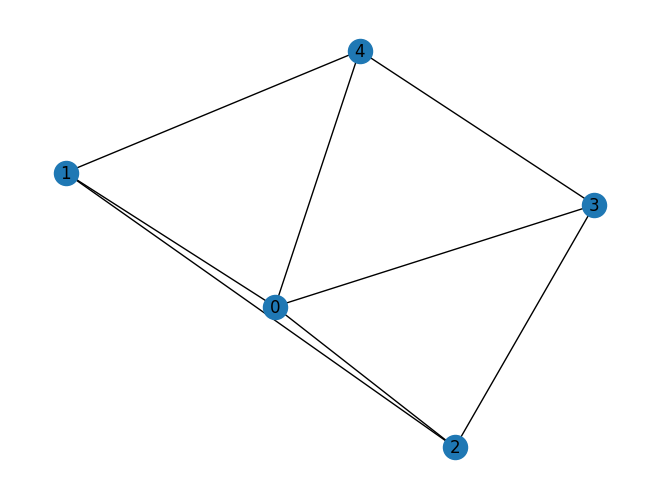
Task 1: Build the graph shown above in networkx using the functions to add graphs. The weight of each edge should correspond to the sum of the node labels it connects.
Task 2: Draw the finished graph with matplotlib.
Exercise 2#
Reconsider the example of the European transmission network graph. Use the following code in a fresh notebook to get started:
url = "https://tubcloud.tu-berlin.de/s/FmFrJkiWpg2QcQA/download/edges.csv"
edges = pd.read_csv(url, index_col=0)
G = nx.from_pandas_edgelist(edges, "bus0", "bus1", edge_attr=["x_pu", "s_nom"])
subgraphs = []
for c in nx.connected_components(G):
subgraphs.append(G.subgraph(c).copy())
Choose one of the subgraphs (each representing a synchronous zone) and perform the following analyses:
Task 1: Determine the number of transmission lines and buses.
Task 2: Check whether the network is planar.
Task 3: Calculate the average number of transmission lines connecting to a bus.
Task 4: Determine the number of cycles forming the cycle basis.
Task 5: Create a histogram of the length of the cycles (i.e. number of edges per cycle) in the cycle basis.
Task 6: Calculate the average length of the cycles in the cycle basis.
Task 7: Obtain the directed adjacency matrix.
Task 8: Obtain the directed incidence matrix.